Revolutionizing the Plant- Based Protein Industry with Seaweed
Seaweeds are nothing too fancy, but algae that cultivate in the sea. It has been found out in the researches that what primarily were measured to be indigestible and fish food, is a good source of proteins and other micronutrients.
Some of the experts have their own say on an unusual type of seaweed, called red seaweed. They have one of the maximum protein levels, actually about five times higher than soyabean which once lead the pack in the plant-based protein industry. Likewise, the red seaweeds have an umami flavor, which is associated with meat products.
One more factor which will help seaweed protein to substitute meat-based protein is that the supply chains for red seaweed are hale and hearty. That is due to the fact that red seaweed is by now being used as an ingredient in numerous daily-use products, such as ice creams, toothpastes, etc.
Though, in these cases, seaweeds are a source of carrageenan and agar, not protein. But, if leading companies invest in research and development of extraction methods of protein from seaweeds, the already prevailing supply chains can make the process more efficient.
Therefore, red seaweeds are surely more liked by people, than any other plant-based meat products, for replacing actual meat-based products because of numerous factors, such as delicious taste, high protein content, and good supply chains.
Nutrients Provided by Seaweeds
Seaweeds are excellent source of plant-based proteins, or precisely seaweed proteins, but deliver numerous other micronutrients essential for everyday functioning of the body. Some of them are listed below:
Antioxidants
They are essential for the human body, as they aid in nullifying the effect of free radicals accountable for numerous ailments, such as heart ailments, diabetes, etc. Apart from antioxidants including vitamin C, A and E, seaweeds also are a rich source of carotenoids, such as fucoxanthin helping in an improved protection of cell membranes.
Iodine and Tyrosine
Seaweeds have a lot of iodine, mostly owing to their capability of absorbing iodine, present in their natural surroundings, i.e., the oceans. Accompanied by iodine, seaweeds also have tyrosine, an important chemical for production of diverse brain chemicals, such as dopamine and epinephrine. Moreover, both iodine and tyrosine, help in smooth functioning of thyroid gland.
Polysaccharides
Seaweeds contain sulfated polysaccharides known to help in increasing the “good” bacteria in the stomach. Accompanied by this, polysaccharides also support in the production of short-chain fatty acids which improve the overall gut health. Therefore, polysaccharides, and eventually seaweeds, supporting in the process of digestion in the body.
Seaweed proteins are surely taking over the plant-based meat. The high cost of extraction of seaweed protein from sea vegetables is still the major roadblock in the overall expansion of the seaweed protein market.
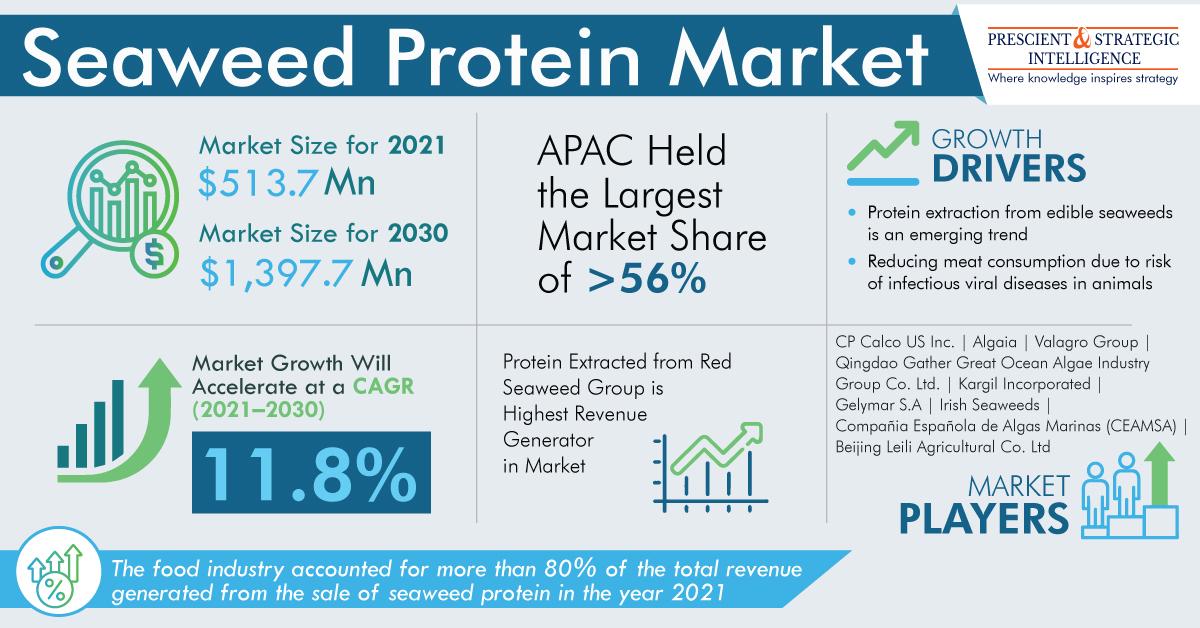
But, nevertheless, because of the growing popularity of seaweed protein among people and a lot of potential in the future, the demand for the same will reach USD 1,397.7 million by 2030.

- Business
- Research
- Energy
- Art
- Causes
- Tech
- Crafts
- crypto
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


