How Are Urban and Semi-Urban Areas Accelerating Adoption of Fixed Wireless Access Solutions?
How Are Urban and Semi-Urban Areas Accelerating Adoption of Fixed Wireless Access Solutions?
Introduction: The New Era of Broadband Connectivity
The digital revolution has reshaped global connectivity needs, driving an urgent demand for faster, more reliable, and affordable internet access. As fiber-optic deployments face logistical and financial barriers, Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) has emerged as a transformative solution for delivering high-speed broadband to homes, businesses, and institutions especially in urban and semi-urban regions where connectivity requirements are rapidly evolving.
According to recent market data, the Fixed Wireless Access Market was valued at USD 171.8 billion in 2024 and is projected to soar to USD 719.2 billion by 2032, expanding at an impressive CAGR of 19.6% during the forecast period. This exponential growth underscores the increasing reliance on wireless broadband technologies as 5G networks mature and governments push for universal digital access.
Urban and semi-urban environments representing the epicentres of digital innovation and economic growth are at the heart of this transition. These areas not only drive adoption through population density and enterprise demand but also serve as early testing grounds for advanced broadband ecosystems integrating 5G, IoT, cloud computing, and smart city infrastructure.
Source: Fixed Wireless Access Market Size, Share and Growth Report 2032
Understanding Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)

Figure 2: Infographic illustrating the components of Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): a base station transmitting a wireless signal to a Customer Premise Equipment (CPE) device installed on a building, highlighting spectrum bands and the core network.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) delivers high-speed internet connectivity using wireless radio links between fixed points typically from a base station to a customer premise equipment (CPE) device. Unlike mobile networks, FWA offers dedicated broadband services through licensed or unlicensed spectrum bands without requiring physical fiber or copper cabling to each end-user.
Key Components:
- Base Station: Connects to a fiber backbone or microwave link.
- Customer Premise Equipment (CPE): Antennas or routers installed on buildings to receive the signal.
- Spectrum Bands: Operates on sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave frequencies (24–39 GHz and above 39 GHz).
- Core Network: Manages authentication, routing, and traffic management for stable service.
Advantages Over Traditional Broadband:
- Faster Deployment: No need for trenching or laying fiber.
- Scalability: Easily expanded to new households or enterprises.
- Cost-Efficiency: Lower infrastructure investment compared to fixed-line broadband.
- Versatility: Supports residential, commercial, industrial, and governmental use cases.
With 5G integration, FWA can now deliver gigabit-level speeds, ultra-low latency, and support bandwidth-heavy applications such as video streaming, telemedicine, and cloud-based remote work solutions.
Market Overview and Growth Drivers
The global FWA market’s growth is rooted in a combination of technological progress, socio-economic transformation, and policy support. Its adoption curve is especially steep in urban and semi-urban zones, where the balance between affordability, performance, and accessibility is driving widespread substitution for traditional broadband options.
1. Rising Demand for High-Speed Internet
The digital economy’s dependence on remote work, cloud computing, and video-based communication has sharply increased data consumption. FWA bridges the gap between high-speed connectivity and ease of deployment, providing an immediate solution for areas with limited fiber reach but high broadband expectations.
2. Rapid 5G Rollout
The expansion of 5G networks significantly enhances FWA’s performance capabilities. Using mmWave and sub-6 GHz frequencies, telecom operators deliver multi-gigabit broadband speeds, supporting everything from AR/VR applications to smart building automation.
3. Government Digital Inclusion Programs
Governments worldwide are implementing initiatives to bridge the digital divide. Urban and semi-urban regions, often located at the fringe of fiber infrastructure, benefit from FWA’s ability to provide affordable, scalable, and reliable broadband key for digital literacy, education, and e-governance.
4. Cost and Time Efficiency
Compared to fiber optic networks, FWA requires significantly less capital expenditure and shorter deployment timelines. This makes it attractive for telecom operators, ISPs, and governments looking for scalable connectivity solutions in rapidly expanding city suburbs and semi-urban districts.
Regional Market Dynamics
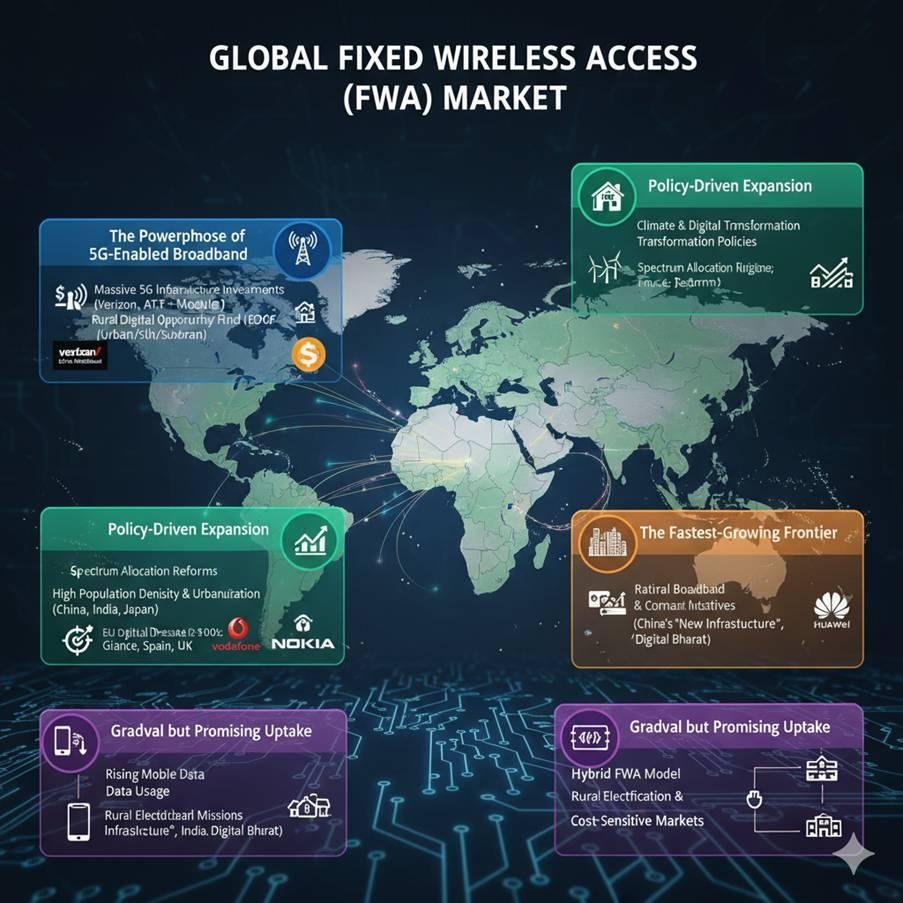
Figure 3: An illustrative world map and infographic showing the Global Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) Market dynamics across four regions: North America (Powerhouse of 5G-Enabled Broadband), Europe (Policy-Driven Expansion), Asia-Pacific (The Fastest-Growing Frontier), and Latin America and MEA (Gradual but Promising Uptake)
1. North America: The Powerhouse of 5G-Enabled Broadband
North America remains the leading region in the Fixed Wireless Access market. The U.S. and Canada are witnessing strong growth due to:
- Massive 5G infrastructure investments by Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile.
- Government-backed digital inclusion programs such as the U.S. “Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF).”
- High consumer demand for gigabit-speed broadband in both urban and suburban areas.
Verizon Communications Inc. has pioneered the use of 5G Ultra-Wideband technology to deliver FWA across American cities, offering speeds exceeding 1 Gbps. Urban deployment is being supplemented by suburban coverage to capture unserved and underserved communities.
2. Europe: Policy-Driven Expansion Across Diverse Terrains
Europe’s FWA growth is supported by:
- Strong climate and digital transformation policies promoting fiber alternatives.
- Spectrum allocation reforms enabling flexible 5G-based deployments.
- Rural and suburban broadband initiatives across Germany, France, Spain, and the UK.
European operators such as Vodafone Group Plc and Nokia Corporation are investing heavily in sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave spectrum utilization, enabling rapid coverage expansion. The European Union’s “Digital Decade” targets 100% gigabit connectivity coverage by 2030, where FWA plays a crucial role.
3. Asia-Pacific: The Fastest-Growing Frontier
Asia-Pacific (APAC) represents the fastest-growing market segment, powered by:
- High population density and rapid urbanization in China, India, and Japan.
- Rising data consumption due to streaming, gaming, and cloud-based services.
- National broadband missions encouraging affordable wireless internet in semi-urban and rural zones.
China’s “New Infrastructure Plan” and India’s “Digital Bharat” initiative are driving record deployments. Local operators supported by global leaders like Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. are leveraging 5G FWA to bring fiber-like speeds without the associated infrastructure costs.
4. Latin America and Middle East & Africa: Gradual but Promising Uptake
While still in the early adoption phase, both Latin America and the Middle East & Africa (MEA) show steady growth driven by:
- Rising mobile data usage.
- Rural electrification and connectivity programs.
- Cost-sensitive markets favoring wireless broadband over expensive fiber installations.
Governments and private telecom firms are collaborating on hybrid FWA models to expand access to schools, hospitals, and small enterprises, fostering economic inclusion.
Technological Advancements Shaping Urban and Semi-Urban FWA
The success of FWA in densely populated environments depends heavily on technological innovation. The market is witnessing breakthroughs that enhance performance, cost-effectiveness, and scalability.
1. 5G-Integrated Fixed Wireless Systems
5G integration provides unprecedented bandwidth and low latency. Urban and semi-urban operators deploy beamforming, massive MIMO, and carrier aggregation technologies to improve signal quality and extend coverage.
2. Hybrid Broadband Models
Modern FWA networks are combining wireless and fiber backhaul, creating hybrid systems capable of handling high data loads while maintaining consistent uptime—ideal for multi-user environments like apartment complexes or office clusters.
3. Intelligent Spectrum Utilization
Dynamic spectrum sharing enables operators to use both licensed and unlicensed bands efficiently. This is critical in urban areas where frequency congestion is common.
4. AI and Network Optimization
Artificial Intelligence-driven network management optimizes bandwidth allocation, predicts congestion, and improves user experience—especially essential for managing heavy data traffic in urban zones.
5. Energy-Efficient Infrastructure
Sustainability is becoming a priority. New antenna designs and energy-optimized CPE devices reduce operational costs and carbon footprint, supporting green city initiatives.
Application Segments: How FWA Serves Multiple Sectors
The Fixed Wireless Access market is segmented by application across residential, commercial, industrial, and government sectors—each driving adoption through distinct use cases.
1. Residential Sector
Urban households increasingly depend on high-speed internet for entertainment, remote work, and education. FWA provides a stable, low-latency alternative to wired broadband, particularly in newly developed housing clusters.
2. Commercial Sector
Businesses leverage FWA to support POS systems, surveillance networks, and cloud-based operations. Semi-urban retail chains, co-working spaces, and small enterprises find FWA cost-effective compared to leased fiber lines.
3. Industrial Sector
Factories and warehouses located outside city cores use FWA for automation, IoT integration, and remote monitoring. Its scalability enables real-time data analytics essential for Industry 4.0 operations.
4. Government and Public Sector
Governments deploy FWA to enhance public Wi-Fi zones, smart city infrastructure, and emergency communication networks all critical components of digital transformation agendas.
Key Market Players and Competitive Landscape
The FWA ecosystem is highly competitive and innovation-driven. Major companies are investing in R&D, partnerships, and large-scale network rollouts to capture market share.
|
Company |
Key Focus Areas |
|
Verizon Communications Inc. (U.S.) |
5G Ultra-Wideband FWA expansion across North America |
|
Nokia Corporation (Finland) |
Turnkey FWA solutions integrating 5G, mmWave, and AI optimization |
|
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. (China) |
Global 5G infrastructure leadership and semi-urban coverage expansion |
|
Vodafone Group Plc (UK) |
Spectrum investments and urban broadband initiatives in Europe |
|
Ericsson AB (Sweden) |
Advanced FWA platforms supporting multi-gigabit urban connectivity |
These companies are shaping the global landscape through product innovation, spectrum partnerships, and region-specific service models, ensuring broader access and improved user experiences.
Challenges and Restraints
Despite its rapid growth, the FWA market faces several challenges that influence scalability and profitability:
- Spectrum Availability: Limited licensed spectrum bands in some regions constrain capacity.
- Deployment Costs: High initial costs for 5G infrastructure may restrict expansion in developing economies.
- Competition from Fiber and Satellite Broadband: Fiber offers higher reliability, while satellite internet (e.g., Starlink) provides wide-area coverage, challenging FWA adoption in remote regions.
- Line-of-Sight Limitations: Urban obstructions such as buildings can affect signal strength and require advanced network planning.
Nevertheless, ongoing innovation in antenna design, beamforming, and hybrid deployment models continues to mitigate these limitations.
Future Outlook: The Road Ahead for FWA in Urban and Semi-Urban Zones
The future of Fixed Wireless Access lies in 5G maturity, smart city integration, and digital inclusivity. As urban and semi-urban areas become more connected, FWA will play a pivotal role in supporting:
- Next-generation smart homes and IoT devices.
- Public digital infrastructure such as intelligent transport and security systems.
- Sustainable connectivity with energy-efficient and recyclable materials.
By 2032, FWA is expected to contribute substantially to universal broadband access goals, complementing fiber networks rather than competing with them forming a hybrid model that ensures seamless connectivity across all geographies.
Conclusion
Urban and semi-urban areas stand at the forefront of the Fixed Wireless Access revolution, accelerating its global adoption through technological readiness, policy support, and user demand for fast, flexible, and affordable broadband. The surge from USD 171.8 billion in 2024 to USD 719.2 billion by 2032 reflects a seismic transformation in how the world connects moving toward a wireless-first era powered by 5G innovation, smart city development, and inclusive digital infrastructure.
As governments, telecom providers, and technology giants continue investing in scalable and sustainable connectivity, Fixed Wireless Access is not just bridging the digital divide it is redefining the future of global broadband ecosystems, ensuring that connectivity becomes not a privilege, but a universal right.
Source: Fixed Wireless Access Market Size, Share and Growth Report 2032
- Business
- Research
- Energy
- Art
- Causes
- Tech
- Crafts
- crypto
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


